An intrauterine (IUD) has become one of the most popular method of birth control due to its advantages and a few side-effects and complications. It has its effiency, reliability and comfort. Since it can be used for many years, an IUD is much cheaper method of contraception compared to other available ones.
Advantages of IUD
First of all it is a device of high efficiency in protecting from pregnancy. It has the effectiveness of 99% if inserted properly. An IUD becomes effective from the moment of its insertion into the uterus. In addition it provides continuous protection from pregnancy for five or twelve years, depending on the type of a device. It is especially comfortable to women, who do not have to care about birth control every time they have sexual intercourse.
Once inserted into the uterus, an IUD cannot be felt by a woman or her partner, therefore gives no inconveniences during sexual intercourse. Women, who do not wish to use a hormonal method of contraception, can choose a copper containing intrauterine device that is as effective as the one releasing hormones. Also it is very convenient to breast-feeding women since the device does not interfere with this period and is totally safe both for a woman and her baby.
A hormone releasing type of intrauterine device also make women’s period bleeding lighter and shorter. It is also said to reduce muscle cramps during menstrual period. In addition, a copper containing intrauterine device can be used as a method of emergency contraception. It is claimed to have the efficiency of 99% if used within five days of vaginal intercourse.
Complications of intrauterine device
As with all methods of contraception there are a few side effects and complications associated with the use of an intrauterine device. A copper containing intrauterine device can cause a harder and more intense bleeding during menstrual period. Although rarely, but to some women this could cause anemia. Additionally, this type of an intrauterine device my cause spotting and more painful muscle cramps during period. A hormone releasing intrauterine device may have the same side effects as a birth control pill, since its side effects are associated with the release of hormones. Although insertion of an IUD is most frequently painless, some women claim it to be painful.
Complications associated with the use of an intrauterine device are said to be rare but possible, therefore women should be aware of all possible complications before choosing this method of birth control. There is a risk of 0.003% of the puncture of the uterus during insertion of an IUD. Usually this complication is noticed by a gynecologist right away. Women should be aware that there is a possibility that an IUD could fell out of the uterus. Usually 7 out of a hundred women using this form of contraception experience the expulsion of an intrauterine device within the first year or the first month after insertion of an IUD . If a woman does not notice it she can become pregnant since she is fertile straight away after the expulsion.
Another complication that is rather rare but still can occur is an infection since normal bacteria of the vagina can get into the uterus during insertion of an IUD and cause a uterine infection. Most infections can be cured with antibiotics but some may need surgical therapy leaving a woman sterile afterwards. There is also a higher risk for inflammatory pelvic disease.
And finally another condition that needs additional attention is an IUD and pregnancy. If a woman becomes pregnant with a uterine device present in her uterus there is a higher risk for ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage, inflammatory pelvic disease and preterm labor. If a woman becomes pregnant with an IUD present, this device should be taken out by a gynecologist.
 An intrauterine device (or just IUD) becomes a very popular
An intrauterine device (or just IUD) becomes a very popular  ParaGard T 380A is a T-shaped intrauterine device that contains copper and is used in
ParaGard T 380A is a T-shaped intrauterine device that contains copper and is used in 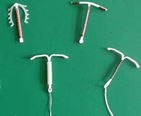 The most frequent reason why the
The most frequent reason why the  An intrauterine device, mostly known as an IUD, is a flexible device that protects from unexpected pregnancy when inserted into a woman’s uterus through the vagina. An IUD is one of the most popular methods of birth control among fertile women worldwide. Some statistics claim that approximately 15% of all fertile women in the world choose an intrauterine device to protect from pregnancy. This is an effective, comfortable and long-term method of contraception for fertile women.
An intrauterine device, mostly known as an IUD, is a flexible device that protects from unexpected pregnancy when inserted into a woman’s uterus through the vagina. An IUD is one of the most popular methods of birth control among fertile women worldwide. Some statistics claim that approximately 15% of all fertile women in the world choose an intrauterine device to protect from pregnancy. This is an effective, comfortable and long-term method of contraception for fertile women. Women should be aware that an
Women should be aware that an 
 Most data suggests that a woman regains fertility immediately after the removal of IUD. Some claim that pregnancy is possible after one month after the removal of this device from the uterus. Women should be aware that there are certain differences between a copper and hormonal IUD and should discuss all the pros and cons with the doctor prior to insertion of this contraceptive device into the uterus.
Most data suggests that a woman regains fertility immediately after the removal of IUD. Some claim that pregnancy is possible after one month after the removal of this device from the uterus. Women should be aware that there are certain differences between a copper and hormonal IUD and should discuss all the pros and cons with the doctor prior to insertion of this contraceptive device into the uterus. 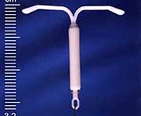 Mirena is levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system. It is a hormonal
Mirena is levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system. It is a hormonal