Imagine the situation: you come home from work after a terribly long day during which your female boss was scolding you all day long, your secretary got insulted and burst into tears when you asked her to bring you a cup of morning coffee, and finally your wife/better half/lover locked herself in your bedroom in front of TV with a giant jar of chocolate-peanut butter ice-cream. Have you tried asking “What’s wrong?” Did it get worse? I bet it did.
PMS medicine
 This is what the male friends, colleagues, acquaintances, and life partners of more than 45 million women worldwide are going through at least once a month: they have to deal with all possible women’s mood changes caused by anxiety, depression, cramps, heaviness and headache. They feel irritable, start crying without reason, find themselves confused, lost, clumsy, absent-minded, withdrawn, and paranoid and even have suicidal thoughts. They don’t feel beautiful and if one tries to compliment them, everything turns to another drama on the monthly basis.
This is what the male friends, colleagues, acquaintances, and life partners of more than 45 million women worldwide are going through at least once a month: they have to deal with all possible women’s mood changes caused by anxiety, depression, cramps, heaviness and headache. They feel irritable, start crying without reason, find themselves confused, lost, clumsy, absent-minded, withdrawn, and paranoid and even have suicidal thoughts. They don’t feel beautiful and if one tries to compliment them, everything turns to another drama on the monthly basis.
Don’t be surprised when the conversation with the verbal and physical expression of sympathy, care and love will turn into the outpouring of the swearwords, names and reasonless charges. Does something like ‘I need a hug, GET LOST!, I miss you, I WANNA BE ALONE!, kiss me, I HATE YOU!’ uttered at the same time sound familiar to you? I wouldn’t be surprised if the only thing you would want to ask in the situation like this would be ‘Honey please make sense!’
PMS symptoms
Unfortunately, we don’t know the exact reasons of PMS are unknown. It is also unknown why some of us can go into extremes, some have fairly mild symptoms, and others do not feel anything at all. However, doctors believe that PMS, depression and physical discomfort has something to do with neurochemical changes in women’s brain.
Recent studies proved that female hormone estrogen makes its contribution to PMS as well. It has a feature of increasing brain activity and action of the heart. It also explains why some women tend to gain wait before their period starts, which definitely is one more reason for a woman to feel irritated and out of control.
You Can Avoid It, if You’re… Lucky
The more you try to make the situation better, the less successful you are. It’s one more of those general truths. You may try to approach a woman with a PMS symptoms by making jokes and using such euphemistic words as Aunt Flo, Monthly Visitor, Special Friend etc.; you may pretend that you understand and support her, you may constantly tell her how beautiful, lovely and fabulous she is, but none of that would work. The only thing that might help is consulting the calendar and getting yourself emotionally ready for the upcoming outburst of PMS symptoms. You might be lucky and get it right! And in case you didn’t, it would at least be a good reminder of when to go to the store and get some chocolate, ice-cream and chocolate chip cookie dough. Take a deep breath man and go, just go!
 6.1 million of adults are infertile in the United States. One third of cases is due to female infertility, another one third accounts for male infertility, 15% of infertile cases is due to the factors of both partners and the rest is considered to be unexplained cases.
6.1 million of adults are infertile in the United States. One third of cases is due to female infertility, another one third accounts for male infertility, 15% of infertile cases is due to the factors of both partners and the rest is considered to be unexplained cases. Menopause literally means the last menstruation. Menstruation usually stops because the levels of estrogen and progesterone are so low that they are not able to stimulate endometrium and it becomes very thin and, hence, does not bleed. Usually
Menopause literally means the last menstruation. Menstruation usually stops because the levels of estrogen and progesterone are so low that they are not able to stimulate endometrium and it becomes very thin and, hence, does not bleed. Usually 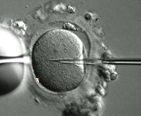 In vitro fertilization procedure has several stages. A woman has to undergo two week long intensive preparation in order to receive several healthy eggs for the procedure. A woman will have to take hormonal preparations during this period. The doctor will know the exact time for taking the eggs from the ovaries by performing blood tests and ultrasound scan of the ovaries. The proper time to take the eggs is just before the ovulation, when the eggs are nearly ready to be fertilized.
In vitro fertilization procedure has several stages. A woman has to undergo two week long intensive preparation in order to receive several healthy eggs for the procedure. A woman will have to take hormonal preparations during this period. The doctor will know the exact time for taking the eggs from the ovaries by performing blood tests and ultrasound scan of the ovaries. The proper time to take the eggs is just before the ovulation, when the eggs are nearly ready to be fertilized.  Statistics shows that 60% of teenage women and 70% of teenage men are already sexually active by their 18th Birthday. 75% of teenage pregnancies are unintended, and 25% of these pregnancies end up in abortion. Most of teenage pregnancies happen because of an early beginning of sexual life, low use of
Statistics shows that 60% of teenage women and 70% of teenage men are already sexually active by their 18th Birthday. 75% of teenage pregnancies are unintended, and 25% of these pregnancies end up in abortion. Most of teenage pregnancies happen because of an early beginning of sexual life, low use of  Although your body gradually becomes the same as the one of an adult during adolescence, it does not mean that you are ready to face the problems of a grown-up life. Therefore it is important to make a decision about sex. It is not easy for anyone and you might want to wait until you are fully grown. If you feel that it is too early to have sex than don’t do it and say so.
Although your body gradually becomes the same as the one of an adult during adolescence, it does not mean that you are ready to face the problems of a grown-up life. Therefore it is important to make a decision about sex. It is not easy for anyone and you might want to wait until you are fully grown. If you feel that it is too early to have sex than don’t do it and say so. Taking care of your health is very important. Regular visits to your general practitioner as well as to a gynecologist are must if you care about your body and want to stay healthy. Specialists say that women need to see their gynecologist at least once a year since the beginning of their sexual life. Others say that it is important to have a
Taking care of your health is very important. Regular visits to your general practitioner as well as to a gynecologist are must if you care about your body and want to stay healthy. Specialists say that women need to see their gynecologist at least once a year since the beginning of their sexual life. Others say that it is important to have a